若图片有问题,请点击此处查看
本文讲PriorityBlockingQueue(优先阻塞队列)
1. 介绍
一个无界的具有优先级的阻塞队列,使用跟PriorityQueue相同的顺序规则,默认顺序是自然顺序(从小到大)。若传入的对象,不支持比较将报错( ClassCastException)。不允许null。 底层使用的是基于数组的平衡二叉树堆实现(它的优先级的实现)。 公共方法使用单锁ReetrantLock保证线程的安全性。
1.1 类结构
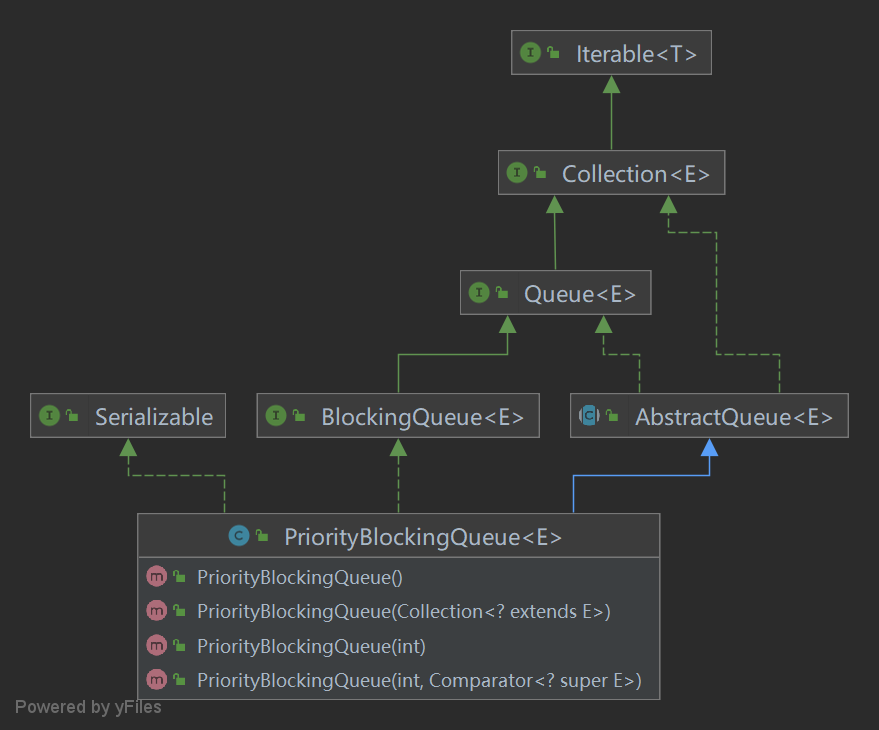
- PriorityBlockingQueue类图
重要的参数
1 | |
保证线程安全的措施
1 | |
2. 源码剖析
我们知道PriorityBlockingQueue实现了BlockingQueue,这篇博客有提到过BlockingQueue可以看一下,它定义了四种方式,对不能立即满足条件的不同的方法,有不同的处理方式。
我们一起去看看下面几种类型的方法的具体实现
- 入队
- 出队
2.1 入队
1 | |
上面几个入队方法都是去调用的offer(e),所以主要来看看这个方法的实现吧
1 | |
总体步骤很简单,查看是否需要扩容,然后再插入元素到二叉堆里。我们看看扩容的实现
- 扩容
容量小于64,oldCap + (oldCap + 2); 否则oldCap + (oldCap * 0.5)
1 | |
为什么扩容时,会解锁,并通过CAS去进行新容量的计算?
However, allocation during resizing uses a simple spinlock (used only while not holding main lock) in order to allow takes to operate concurrently with allocation.This avoids repeated postponement of waiting consumers and consequent element build-up.
上面的话,大致意思就是,扩容时使用自旋锁而不是lock,为了在扩容时,也可以执行出队操作(上面的代码中,扩容比较耗费时间)。避免让阻塞的消费者被反复阻塞(被唤醒后,不满足条件,又被阻塞,反复)。 Doug Lea 👍👍
2.2 出队
只讲poll()的实现;take()与poll(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)的实现都差不多
1 | |
我们先看二叉堆的插入方法siftUpComparable,再看dequeue。
1 | |
这个二叉堆是小根堆(任何一个结点的左右子节点的值都大于自己)
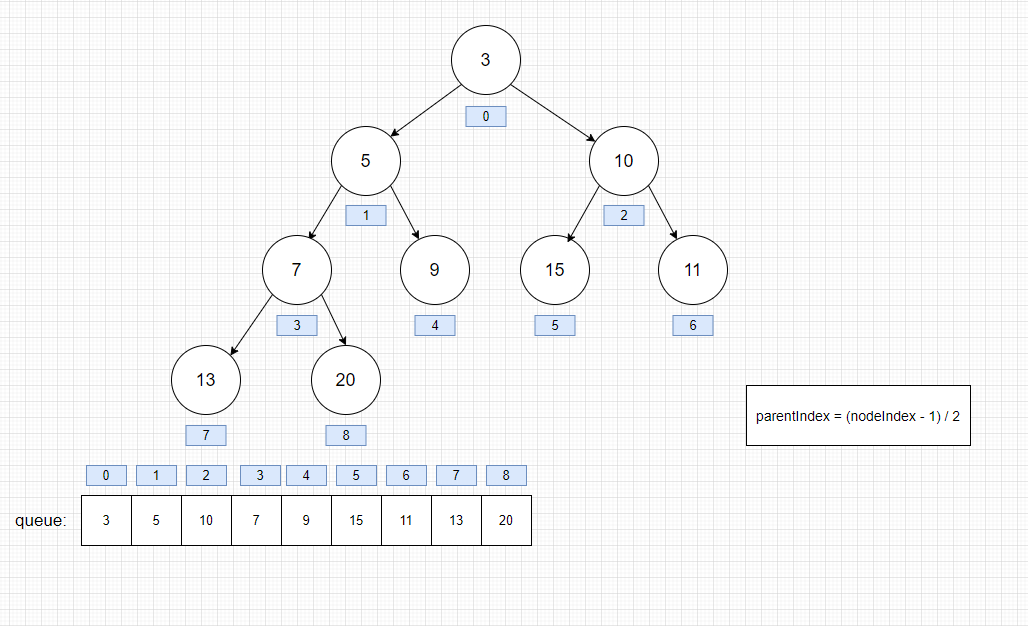
- 堆初始化
此时,我们执行offer(4)。按照上面的源码,我们最后得到
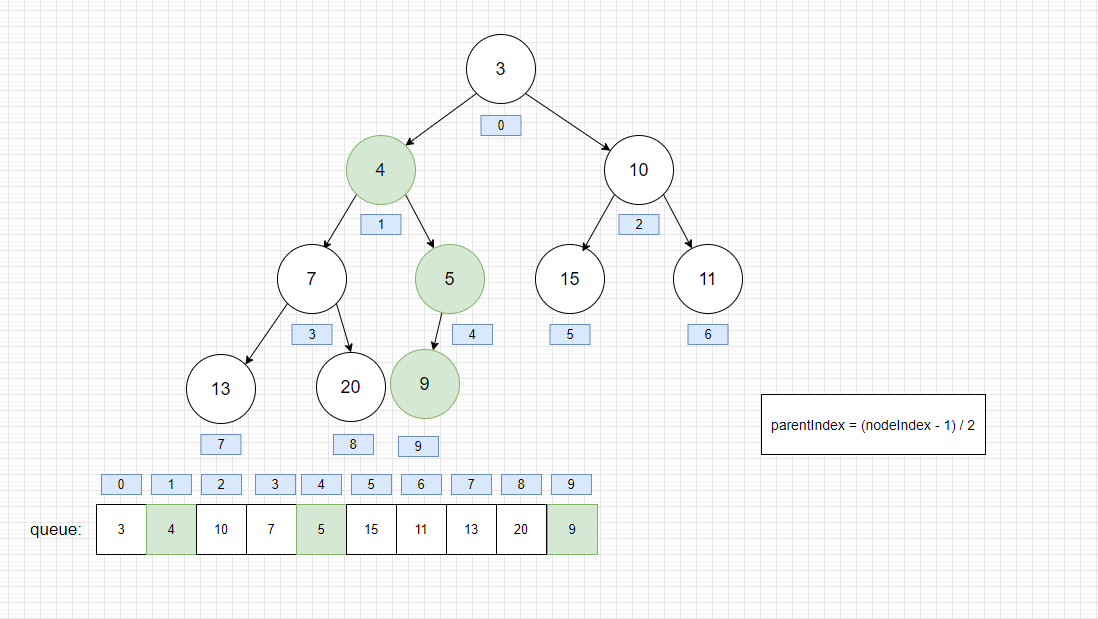
- offer(4)
整个堆插入的思路: 欲插入的元素是否比其父结点小,则与父结点互相交换(小根堆)
我们再执行poll() -> dequeue()
返回头部元素,然后重新调整堆元素位置 ```java
1 | |
将 x元素插入到k位置,为了维持二叉堆的平衡,一直降级x直到它小于或等于它的子节点
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21private static <T> void siftDownComparable(int k, T x, Object[] array, int n) { if (n > 0) { Comparable<? super T> key = (Comparable<? super T>)x; int half = n >>> 1; // half = n / 2 // loop while a non-leaf while (k < half) { int child = (k << 1) + 1; // assume left child is least child = k * 2 + 1 Object c = array[child]; int right = child + 1; if (right < n && ((Comparable<? super T>) c).compareTo((T) array[right]) > 0) // 左右节点谁小,谁就当父结点 c = array[child = right]; if (key.compareTo((T) c) <= 0) break; array[k] = c; k = child; } array[k] = key; } }
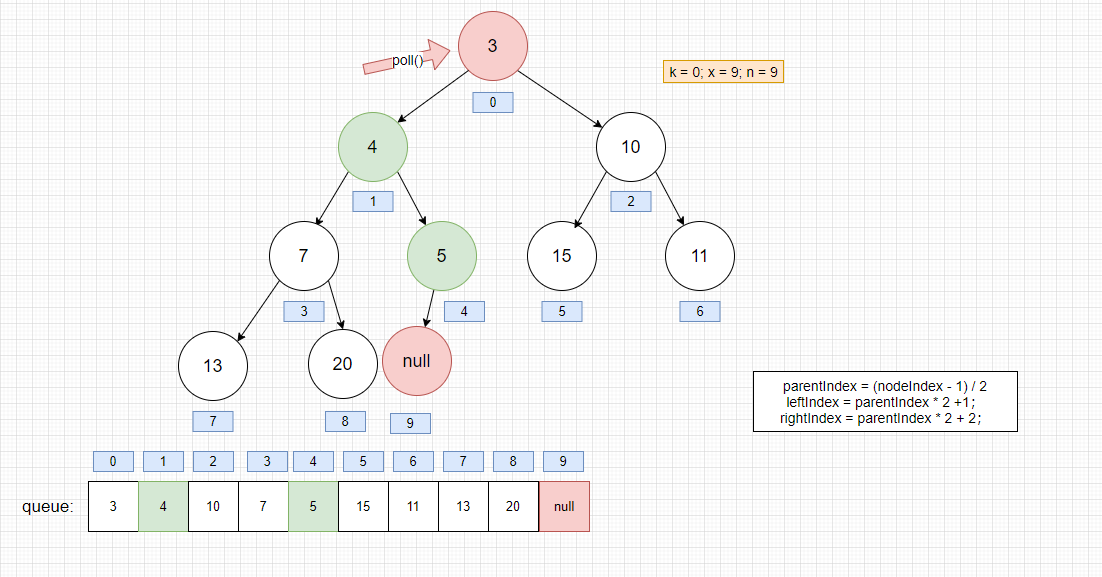
- 进入siftDownComparable的状态
执行完毕
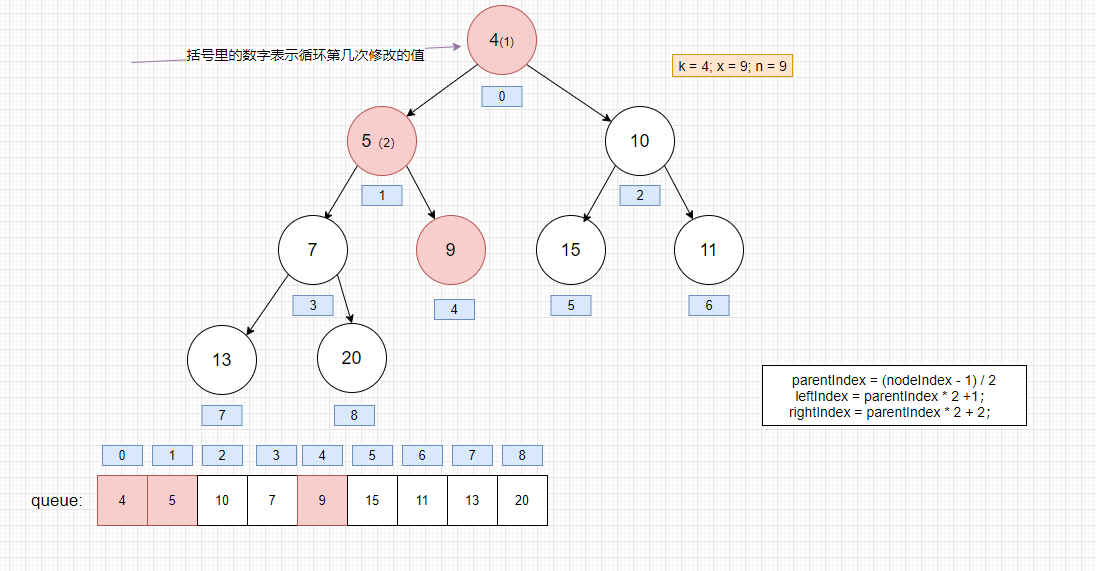
堆获取头结点后的思路: 将最后一个节点保存起来并置空,将它插入到第一个节点,若不满足就执行下面的流程.
- 比较第一个节点的左右节点是否小于该节点,是的话,就交换左右节点的最小的一个值的位置,周而复始。直到满足最小堆的性质为止
3. 总结
- PriorityBlockingQueue入队后的元素的顺序是按照元素的自然顺序(Comparator为null时)进行维护的。
- 使用ReetrantLock单锁,保证线程的安全性;在扩容时,通过CAS来保证只有一个线程可以成功扩容,同时扩容时,还可以进行出队操作
- 顺序通过二叉堆维护的,默认是最小堆
4. 参考
- 深入理解Java PriorityQueue – 对堆的算法讲的很细致